Analysis of Positive Trends in the Volkswagen Auto Parts Industry
As the global automotive industry rapidly enters the era of new energy and intelligence, Volkswagen, as a leading global vehicle manufacturer, is constantly adjusting and upgrading its supporting parts system. In major overseas markets such as Europe and North America, the mass accessories industry is showing a series of positive trends, covering aspects such as intelligent manufacturing, software integration, modular platforms and supply chain resilience, bringing new opportunities to global supply chain and accessories enterprises.
1. Intelligent manufacturing enhances quality and response capabilities
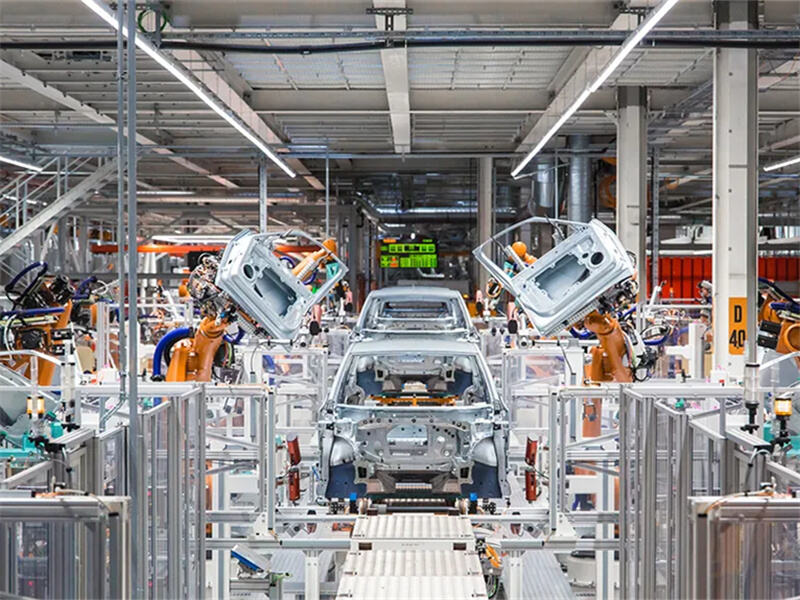
At its production bases in Europe and the United States, Volkswagen is significantly enhancing the production efficiency and quality stability of components through intelligent manufacturing technologies. For instance, it has collaborated with Siemens to deploy "digital twin" technology in multiple accessory links, achieving full-process simulation and real-time optimization from design to manufacturing.
In addition, automated inspection equipment, industrial robots, MES systems (Manufacturing Execution Systems), etc. are widely applied in the assembly and quality inspection processes of components, significantly reducing the rework rate and improving the response speed. Accessory enterprises are also transforming from traditional processing and manufacturing to "digital-driven manufacturing", gradually achieving a highly flexible and modular production model.

Intelligent manufacturing not only enhances the consistency of component shipments but also provides a solid support for the public to accelerate the product update cycle.
Second, the integration of software and hardware enhances the added value of accessories
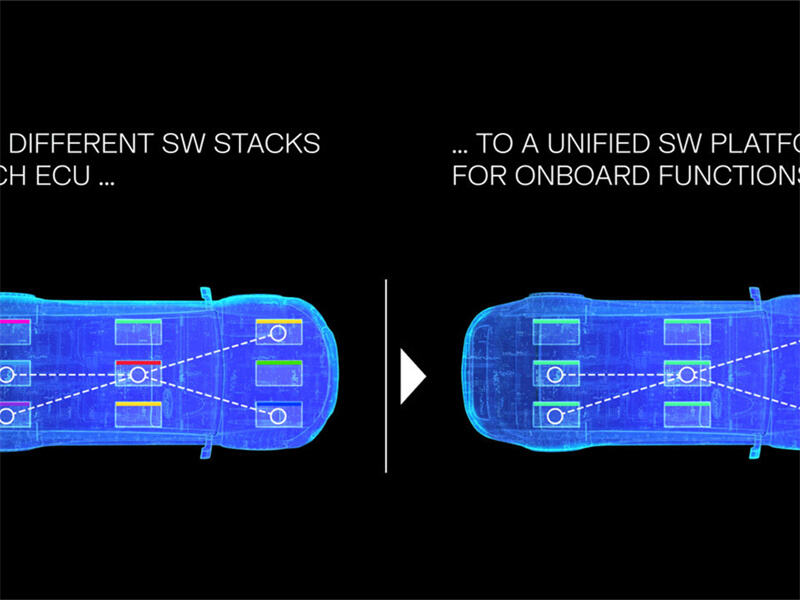
With the upgrade of Volkswagen's electronic and electrical architecture, vehicle components are no longer merely "physical parts"; an increasing number of components have taken on software functions. For instance, intelligent lighting systems, autonomous driving sensor modules, thermal management control units, etc., all integrate embedded control logic and OTA (Remote Update) capabilities.
Volkswagen is promoting the deep integration of "hardware + software platformization" through its software subsidiary CARIAD. This means that accessory enterprises not only need to provide high-quality physical components, but also must participate in functional testing, CAN communication adaptation, and even the embedding and update of security algorithms.
Accessory suppliers with the ability to integrate software and hardware will become an indispensable part of Volkswagen's global future platform, which also means higher profit margins and stronger cooperation stickiness.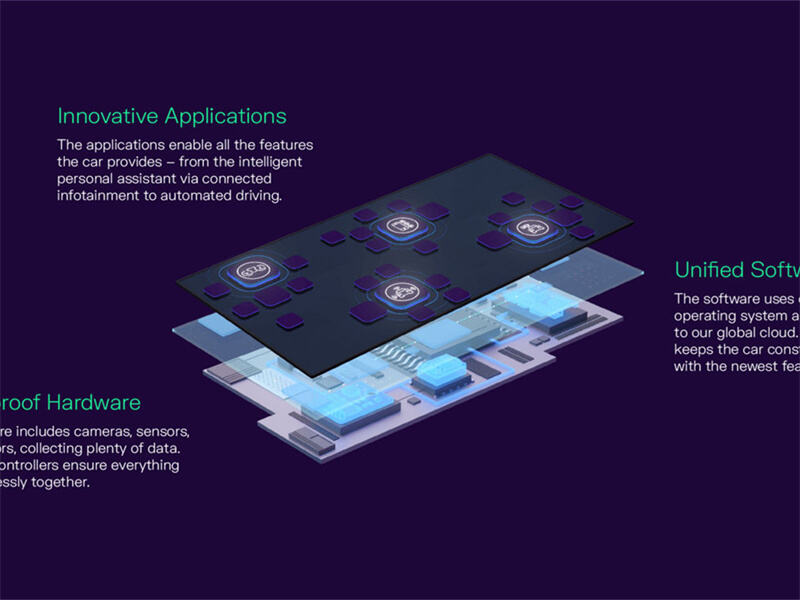
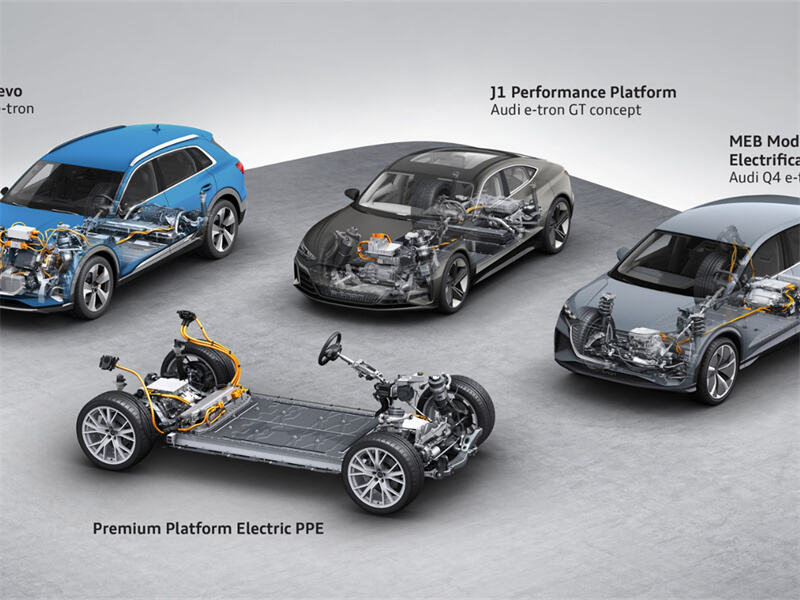
Iii. The modular platform promotes the standardization of accessories
In recent years, Volkswagen has concentrated its resources on developing modular platforms such as MEB and SSP, emphasizing the sharing of core architectures among multiple models. This platform strategy has had a positive impact on the accessories industry:
The types of accessories have decreased but the standards have become higher, promoting batch manufacturing and cost optimization.
Shortening the R&D cycle of parts is conducive to suppliers adapting to new vehicle models more quickly.
The supply of components will revolve around the "platform certification" system, and the cooperative relationship will be closer.
For instance, components such as the electric drive system, heat pump air conditioning, and electronic control motor under the MEB platform can all be reused in multiple vehicle models, enabling suppliers specializing in certain core components to increase order scale and production efficiency.

Fourth, the global supply chain resilience strategy enhances the space for cooperation
The pandemic and geopolitical factors have exposed the vulnerability of the global automotive supply chain. To this end, Volkswagen has adopted a diversified supply strategy in Europe and North America, strengthened regional production layout, established strategic inventories, and enhanced direct control over key components.
This has prompted Volkswagen to seek more cooperation with local parts enterprises in non-Chinese production areas, giving priority to purchasing components from Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, Mexico and other places. For local small and medium-sized enterprises that meet ESG standards and have intelligent manufacturing capabilities, this trend presents a great opportunity to join Volkswagen's core supply chain.
At the same time, the public's emphasis on the "dual-supplier system" has also increased, providing a second supplier opportunity for similar components and bringing a fairer and more stable competitive landscape to the market.
Conclusion
Outside the Chinese market, the Volkswagen parts industry is rapidly evolving in areas such as intelligent manufacturing, software integration, modular platform construction, and supply chain resilience. These positive trends not only drive the technological upgrading of the industry but also create unprecedented development space for accessory enterprises worldwide. For enterprises aiming to enter the mass system or expand their market share, closely following platform changes, building digital capabilities and local response mechanisms will be the key to integrating into the future supply chain.